You’re out in the fresh air, relaxing in the summer sun, when you feel a searing pain and realize you’ve been stung. Don’t panic, and have a look around. Learn how identifying bees, wasps, hornets will help you find whether you’re in danger or just uncomfortable.
Bees are the fuzzy tiny pollinators that we are all familiar with. Bees are unlikely to sting unless you disrupt their hive, and their stings are rarely deadly to most humans.
Wasps are more aggressive and territorial, yet their stings are usually just painful rather than fatal. Hornets, however, can deliver a powerful poisonous blow in huge numbers. Their stings may be deadly, especially for little kids or people allergic to them.
So, don’t panic and swipe in the air the next time something flies past and hurts you. Before reacting, it’s important to determine the source of the danger so you can decide whether to flee, seek medical attention, or shrug it off. Consider this a useful guide to stinging insects and dealing with them without losing calm.
Recognizing Potential Nesting Areas
You may have an unexpected hive nearby if you see any of these signs in your house or near your tent. Keep a distance and be cautious!
Bees may hover around the entrance of their nest, and workers may be seen transporting pollen into the hive. Bees can enter through minor gaps or cracks in walls, eaves, sheds, or trees. The buzzing sound will be more noticeable throughout the day and during the warmer months.
The hexagonal honeycomb structure that bees make to grow larvae and store honey is visible. Honeycomb is often found in wall voids, attics, sheds, and tree hollows.
A swarm of bees, generally controlled by a queen, can assemble on a tree limb, fence, or other surface. They are looking for a new home, so be cautious. The swarm will vanish in a few days.
Bees will fill any fractures or holes in their nesting location. Around the entrances to the hive, you may find a seal made of dirt, chewed wood fibers, or wax.
The wax, honey, and pollen stored inside a functioning beehive can give off a slight honey-like smell. On a hot day, the smell is frequently more prominent.
Wasps and hornets leave similar signals around their breeding sites. Be cautious if you see any of these symptoms since their stings may be deadly. It is better to hire an expert to conduct the removal. Your safety is our number one concern!
Identifying Bees, Wasps, And Hornets
Knowing how to identify bees, wasps, and hornets may actually save your life. Wasps and hornets are more violent and may attack unintentionally. Still, bees are normally gentle and only sting in defense of their hive.
Bees
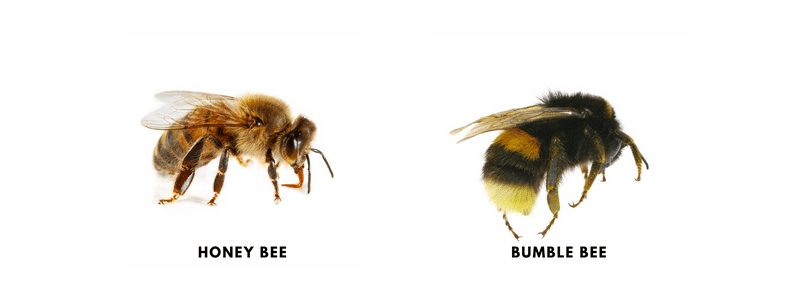
The most frequent varieties are honey bees, bumble bees, and carpenter bees. Bumble and honey bees have soft, spherical bodies with unique color stripes. Carpenter bees have glossy bodies that are predominantly black. Because bees pollinate, they only sting when endangered or their colony is disrupted.
Wasps
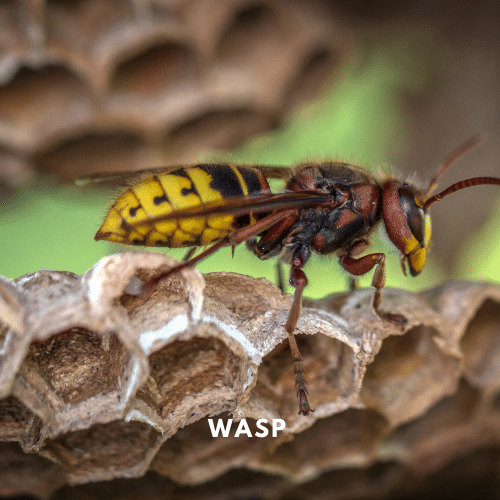

Typical wasps, including yellowjackets, paper wasps, and mud daubers, have long, thin bodies with few or no hairs and distinctive patterns. Mud daubers construct mud nests, whereas yellowjackets and paper wasps construct open-air nests beneath eaves, sheds, or hollow trees. Wasps are hunters and may sting fiercely to protect their nests or to find food.
Hornets
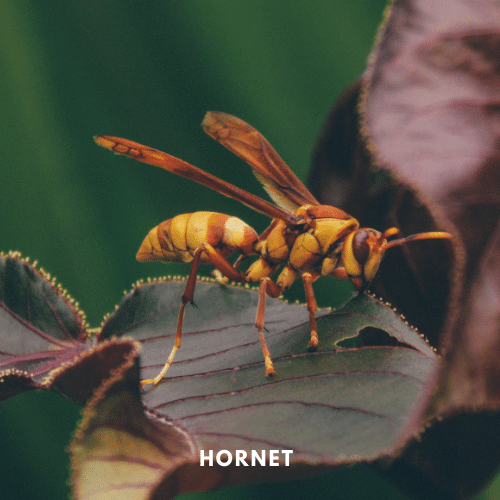

Hornets have big, spherical bodies with white, orange, or yellow markings, such as bald-faced and European hornets. They construct gigantic paper nests in trees or within wall gaps. Hornets are exceedingly aggressive apex predators; their hurting stings may be deadly, particularly for people allergic to them.
When you encounter a bee, wasp, or hornet buzzing about, take note of its traits so you know whether to keep your distance or seek shelter. Precaution is better than cure, so don’t irritate these stinging insects and tread lightly around their nesting areas. You should be better prepared to deal with inappropriate contacts if you can recognize them correctly.
Dangers And Warnings

Bees, wasps, and hornets may be dangerous, particularly if you are sensitive to their venom. Their stings may be very unpleasant and even fatal. It’s essential to be cautious near these insects and their nests.
Allergic Reactions
Anaphylaxis is a severe, sometimes fatal allergic response to a bee, wasp, or hornet sting that may occur in particular people. The symptoms are swelling of the throat or tongue, disorientation, and a drop in blood pressure.
If a sting produces these symptoms, seek emergency medical attention right away. Even those without known allergies can get them at any moment. Thus, all stings should be considered carefully.
Painful Stings
Bee, wasp, and hornet stings are unpleasant but not fatal for most individuals. At the location of the sting, the venom might produce redness, swelling, and irritation. Cold compresses, oral antihistamines, and hydrocortisone lotion may all help alleviate pain. The ache normally goes away within a few hours.
Aggressive Swarms
Bees, wasps, and hornets can become dangerously aggressive when protecting their home. Intentionally disrupting an active nest might result in a colony attack. Their stings are numerous, which increases their toxicity. Never disrupt or push an active nest. To eliminate nests in or near dwellings, contact a professional pest.
Caution Around Nesting Areas
Look for nesting locations such as holes or cracks in attics, beneath decks, inside hollow trees, and under eaves or porches on houses when mowing lawns or trimming plants in areas where nests may be hidden; use care. You should never block or seal off a nest’s entrance since the colony could find another way out and attack.
You can prevent painful stings and even fatal allergic responses by learning the hazards of bees, wasps, and hornets and practicing care near them, particularly in nesting areas. Their stings are sometimes unavoidable, so be prepared to react appropriately in any scenario. Be careful out there!
Tips For Hikers And Backpackers
Identifying bees, wasps, and hornets is important for hikers and backpackers since it might save their life in the event of an encounter. Different species differ in their aggression; some may be dangerous to humans, particularly if they are allergic to bug stings. Here are some precautions to take and how to respond in the event of an attack:
Preventive Measures:
1. Wear suitable clothing: Long-sleeved shirts, long trousers, and closed-toe shoes may be a physical barrier between you and the insects. Because certain bees and wasps are attracted to bright colors, it is best to wear light-colored clothes.
2. Avoiding smells and bright colors: Scented soaps, lotions, and perfumes may attract insects. Additionally, avoid wearing clothes with flowery motifs or bright colors, which may attract bees and wasps.
3. Maintaining calm and silence: When bees or wasps are around, maintaining calm and silence may lessen the probability of drawing their attention. Sudden movements, particularly from more aggressive species, may cause an assault.
Reacting To An Attack:
1. Assessing the situation: If you come into a nest of bees, wasps, or hornets and they get angry, analyze the situation immediately to figure out the degree of danger. It is critical to take action if they begin to swarm or exhibit hostile behavior.
2. Walk away slowly and quietly: If you observe increased curiosity from the insects, try to walk away slowly and gently. Avoid running or making sudden movements since this might cause the insects to attack.
3. Do not swat or squash bees, wasps, or hornets: Avoid the desire to swipe at the insects since this will just excite them and lead to an assault. Avoid crushing them against your body since the aroma may attract others of their type.
Seeking Shelter:
1. Seeking shelter in confined spaces: If you are attacked and unable to flee, attempt to take cover in an enclosed environment such as a building, tent, or car. This may keep the insects at bay until they scatter.
2. Creating a barrier between you and the insects: In the absence of enclosed places, establish a barrier between yourself and the bees, wasps, or hornets using any available items. Use a blanket, bag, sleeping bag or clothes to protect yourself from their stings.
First Aid For Bee, Wasp, Or Hornet Stings:

Determining The Sting’s Severity:
1. Most individuals experience pain, redness, swelling, and itching in the affected area after being stung by a bee, wasp, or hornet. The sting in these circumstances is usually not life-threatening, although it may be unpleasant.
2. However, some people are sensitive to insect stings, which may vary from moderate to severe and life-threatening. To select the best approach, it is critical to analyze the severity of the sting.
General First Aid Steps:
1. Bee sting removal: When a bee hits you, it leaves its stinger behind. Because the stinger continues to deliver poison into the body, removing it as soon as possible is critical. Avoid using tweezers or squeezing the stinger, as this might cause more poison to be released. Instead, use a flat gadget like a credit card or your fingernail to remove it from the skin’s surface.
2. Treat the affected area after removing the stinger: To limit the risk of infection, treat the affected area with mild soap and water.
3. Using a cold compress or an ice pack wrapped in a cloth, apply it to the affected area for around 15 minutes. This can help to alleviate discomfort and swelling.
Tip: Always carry a first aid kit.
Allergic Reactions And Emergency Response:
1. Identifying an allergic response: Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction to bee, wasp, or hornet stings in certain people. Breathing problems, hives, swelling of the face, throat, or tongue, dizziness, fast heart rate, or a decrease in blood pressure are all symptoms of an allergic response.
2. Using an epinephrine auto-injector: If you or another person suffers from allergy symptoms and you have access to an epinephrine auto-injector, use it right away, according to the instructions on the device.
3. Seeking urgent medical assistance: Call 911 or the relevant emergency number in your region after injecting epinephrine, or if an epinephrine auto-injector is not accessible, seek immediate medical attention. Anaphylaxis may be fatal and needs rapid medical attention.
Additional Resources
If you are looking for more tutorials, walkthroughs and troubleshooting about camping and enjoying the outdoors, here are some additional posts to check out:
Conclusion
You now have the expertise to identify those buzzing animals on your lawn. Don’t worry the next time you hear an alarming buzz; instead, observe. Look for signs such as color, size, and nest form to evaluate whether that hovering insect is a threat.
Knowing the correct identification of a bee or wasp may help you avoid being stung and know when to seek medical attention. Some of these flying friends provide valuable services to your garden, so admire them from afar! With your new stinger-spotting abilities, you’ll be the go-to person for all your friends the next time they have an unexpected visitor at their barbecue.
Thanks for reading, If you think I forgot something or if you simply want to share a story or some advice, feel free to leave your comment below, Be safe and have fun.!

